Changes in a currency’s external value can significantly affect a number of macroeconomic results and targets.
Check out also: Perfect Competition And Monopolistic Competition
The exchange rate and inflation:
The exchange rate has a direct and indirect influence on the inflation rate:
⦁ Change in the prices of imported goods and service:
The consumer price index is directly affected. The appreciation of the currency, for instance, usually reduces the costs of the goods, commodities and capital products from imported goods.
Check Out Also: O Level Economics (2281)
⦁ Commodity Prices:
An increase in the sterling-dollar exchange rate had a strong effect on point of selection rates, including oil and vegetables. The price of other products is expensive for a pound. A stronger dollar makes importing these goods more expensive for Britain.
⦁ Changes in the growth of exports:
Higher currency makes selling overseas more difficult due to an increase in relative prices. When export slowdown (price elasticity of demand is important to determine the scale of any demand shifts), then exporters can opt for prices, output reduction, and job reduction.
The Exchange Rate and Unemployment:
An increase in the exchange rate contributes to slower growth of real GDP as net exports decrease and import demand increases. Reducing demand and production will lead to job cuts as businesses seek to reduce costs.
Many work cuts are immediate, as exports shift and import rates have increased in the short term.
Others would be irreversible because the domestic demand is continuously expanded by imports.
This will have a negative impact on the economy through higher exchange rates. Some sectors are more exposed to currency fluctuations than others – for example in sectors that export the high percentage of total production to high prices.
Check Out Also: O Level Economics (2281)
Some Microeconomic Benefits of a Weaker Currency?
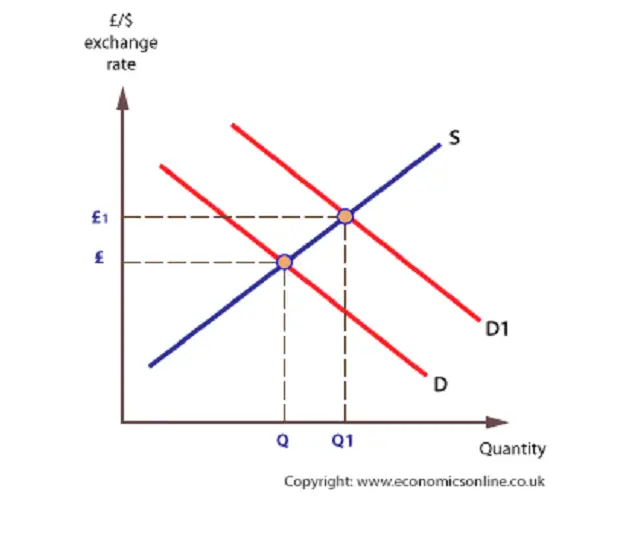
An increase of the exchange rate contributes to slower growth of real GDP as net exports decrease and import demand increases.
Reducing demand and production will lead to job cuts as businesses seek to reduce costs.
Many work cuts are immediate, as exports shift and import rates have increased in the short term. Others would be irreversible because the domestic demand is continuously expanded by imports.
This will have a negative impact on the economy through higher exchange rates. Some industries are more vulnerable to currency fluctuations than others – for example, industries where a large share of the product exports are highly sensitive to demand.