What are the Perfect Competition and Monopolistic Competition?
Two market systems that have a range of main differences in respect to market size, quality stability, and penetration barriers are a single market and a fully competitive market.
Just one company in a monopolistic market controls the quality and availability of products and services and that company has complete control of the market.
Unlike a monopoly market, there are many enterprises on the fully competitive market, in which no firm has any control of the market. No market is completely dominant or fully free in the modern world.
The characteristics of all these types of markets are mixed in every real-world market.
Check Out also: A Level Economics 9708
Difference Between Perfectly Competitive and Monopolistic Market
Perfectly Competitive Market |
Monopolistic Market |
| · Prices are dictated by supply and demand in a market that experiences perfect competition.
· Companies are all decision-makers in an intensely dynamic environment and no organization has adequate market leverage.
· In comparison to a monopolistic economy, businesses have a limited market share in a fully open environment.
· Entry hurdles are fairly low and businesses can quickly reach and leave the market.
· In comparison to monopolies, both consumers and suppliers will pick where to purchase their products and services. The competition is completely competitive. |
· Within a monopoly market, firms become prices as they regulate products and services prices.
· Prices for products and services in this sort of industry typically are large as businesses have complete pricing leverage.
· Companies have a total market share, creating difficult points of entry and exit.
· As there are high obstacles to entry into the monopoly market, companies that manage to enter the market are often dominated by a major company.
· A sole retailer is a monopolistic market and consumers do not have a preference as to where to purchase their products or services.
· It is exceedingly unlikely and perhaps impossible that purely monopolistic economies would be enforced in the absence of total obstacles, including the ban on trade or the exclusive ownership over all-natural resources. |
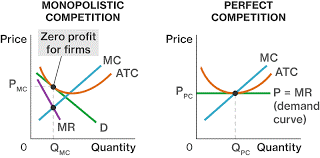
Companies will fix the price of their goods (PMC) on a monopolistic competitive market and gain economic benefit in the short term with each company facing an upturning demand curve (D).
The average total cost (ATC) curve crosses D at this point. The amount of marginal revenue (MR) produced at that price is the marginal cost (MC).
In comparison, businesses cannot change prices (PPC) in a fully competitive market. Prices are determined at marginal income (MR), which is the market’s demand curve. Average total cost (ATC) is also where the marginal cost (MC) crosses the curve.
Effect on Entry of New Firm in Monopolistic Market
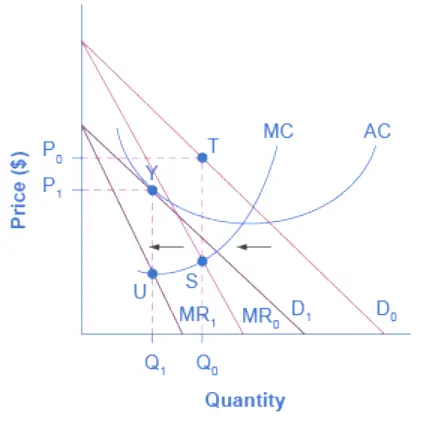
There are little or small entry obstacles in a competitive market, which makes it easier for new entrants to enter the industry.
In such a market, businesses manufacture similar alternatives, which are different between them in several respects (products of equal interest to consumers).
Check Out Also: O Level Economics (2281)
LONG RUN EQUILIBRIUM
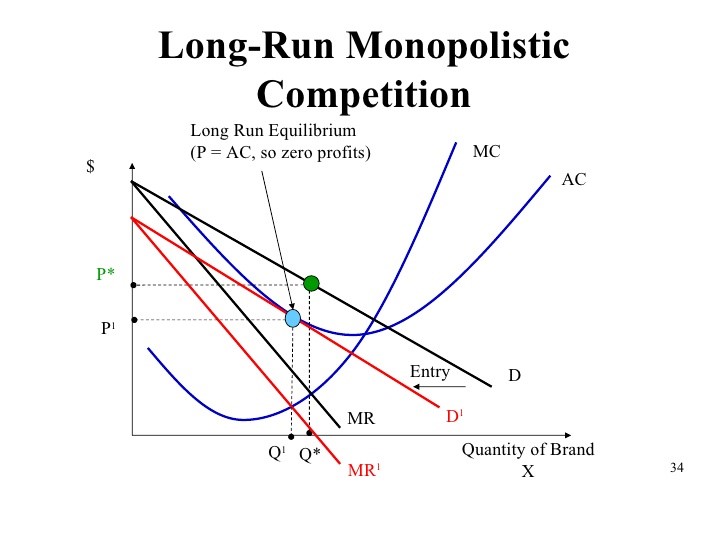
A company leaves a long-term equilibrium where the long-term marginal costs equate to the marginal revenue at a level that corresponds to the output level in which the long-run average cost curve affects the demand curve.
When marginal cost ( MC) is equal to marginal income (MR), price (P) in the long run is identical to the average cost of the total (ATC). The consequence is zero income, which is also known as a regular benefit.

