Resources are distributed in a market dependent on demand and supply in which costs play a signaling role in distributing funds to the output of various types of products.
The monitoring process between purchasers and sellers serves also as well.
Resources are scarce and are unable to manufacture adequate goods and services to fulfill limitless human needs.
The economy must select the types of goods and services it wishes to offer the population.
For example, an economy has to select the different kinds of goods to be purchased jointly by producers and customers using the signaling position and self-interest of prices.
Price demonstrates how many customers, indicated by the demand curve, are eager and ready to pay. The sum of willingness and ability of producers is illustrated by the supply curve.
FOR WHOM TO PRODUCE?
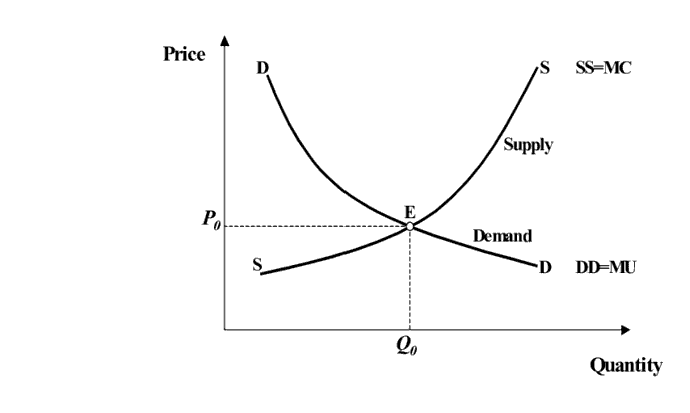
The price process also reveals for whom such goods are to be produced. The demand curve, which implies the willingness and ability of consumers to pay, reflects this.
It reflects their economic dollar votes in any way, indicating suppliers are expected to deliver for these customers.
⦁ Resources are limited, so no organization can fulfill all the people’s wishes.
⦁ How do people share the insufficient availability of finished goods/services?
⦁ Price serves as a consumer economy mechanism that only distributes production to all who will and can pay the good.
This depends in turn on the purchasing power and the value of the goods.
Consumers pay and buy products to improve market protection while producers seek to optimize profits.
HOW TO PRODUCE?
Resource costs and output variables often discuss how specific goods and services are produced. An economy can opt to produce by using specific growth factors, such as labor (human) or capital (machinery).
Resource costs should direct production processes in industries, and businesses should pick the best and the cheapest services.
The manufacturers demand capital in the factor market, and the buyers provide the products with factor shareholders. The resource distribution among the competing uses is focused on resource prices.
for example, A manufacturing commodity may be either made by capital-intensive methods (where there are less effort and more productive use of machinery) or by labor-intensive methods (where there is greater use of labor).
A company’s main objective is to reduce production costs, based on relative prices of production factors. The production of labor-intensive products tends to be involved in countries like China, where there are abundant resources such as LAND and LABOUR, and it is easier to produce with these methods.
Let’s discuss some Advantages and Disadvantages of Market System:
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| • When buyers want a certain product or service, they demand it and prices increase, signaling that the manufacturers are going to manufacture more of it.
Need Help? Ask Our Chat Assistant!• If the producers can generate the necessary quantity of that product, the price would immediately fall to normal.
• Similarly, because consumers don’t like a specific product any longer, they avoid wanting that product, meaning that suppliers no longer profit from producing that good, and suppliers do not produce that good.
• In a market system, manufacturers compete by offering more diverse products. Consequently, consumers can have more choices, and this can even result in lower prices.
• Producer and consumer are the foundation of the market system to decide what to produce, how, and for whom. |
• Unless it is profitable, the company produces no goods or services in a market system.
• In a business economy, commercial businesses are not able to provide such public goods, such as road lights, since any demand is virtually impossible from the customer. the market system does not deliver such products and services.
• If some people want to purchase dangerous goods like drugs, they are ready to buy them, since private companies are prepared to offer anything profitable if businesses and individuals are in a position to produce and consume freely, the rich can be made even richer because they have greater power to take decisions, and the poor can grow poorer because they have less power to make decisions.
• More goods and services are allocated in the market system to consumers with more money than others. |