ECONOMIC PROBLEM
⦁ Both the goods and services that customers use and demand are made up of very few available resources.
⦁ Unlimited and finite resources.
⦁ The basic economic issue is the lack of capital.
Check Out Also: O Level Economics (2281)
FACTOR OF PRODUCTION
⦁ Consumers are individuals or businesses that need products and services and who want them.
⦁ Development instruments or variables are used in the manufacture of goods.
⦁ LAND: Development of natural resources (e.g., land).
⦁ LABOUR: human labor used in goods/services development (e.g. workers).
⦁ The potential and desire to take the risks needed for managing productivity − Businessmen manage, integrate into businesses, resources for goods and services ·
⦁ Sustainable consumer products survive long when (e.g. furniture).
⦁ non-sustainable consumer goods (e.g. food) do not goods and services of capital. Ultimately, the ability of firms to manufacture goods and services (i.e. tractor).
Check Out also: A Level Economics 9708
OPPORTUNITY COST
The term ‘opportunity’ is, in fact, redundant in ‘opportunity cost’. The cost of doing anything is the expense of the most valuable alternative usage instead.
For example, you spend time and money on the movie, you can’t spend the time reading a book in your own house, so you can’t spend money on anything else.
The cost of watching the film is the money invested plus the pleasure that you have missed when the book is not read, meaning that the next possible choice is to watch the video.
⦁ The next possible option forgone is the expense of the product as there is competition even, therefore, those products are forgone for the other.
⦁ This is seen in the production Possible curve diagram:
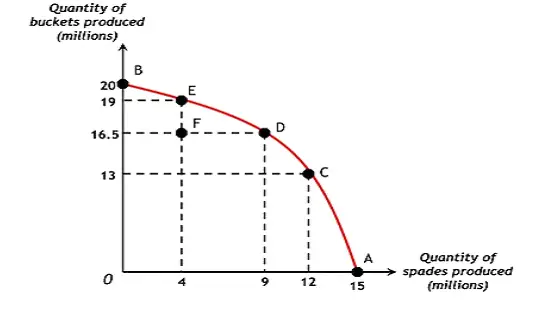
⦁ The curve is regarded as first, but the output capacity curve can never be linear in examples of comparative advantage.
⦁ A curve like a form will still be, as shown in the second diagram.
⦁ As any services extracted from A can’t be used to manufacture B, e.g. employees at a diamond factory are not eliminated and used for the same quality and expertise in the cheese factory, additional rework costs will be incurred.
⦁ Diamond machines still cannot be replaced with cheese machines .
⦁ Thus, the conversion of resources from 2 products is never 100% efficient; therefore, the curve cannot be linear.
⦁ At first, the most competent resources for B are distributed more or less competent for A good to prevent a low cost, however, the most efficient resource for A is moved to B and thus opportunity costs are very high.
⦁ Example 2: An individual spends $10,000 in stock the opportunity cost of investing in the stock is of the value of the future interest of keeping $10,000 in a bank account instead.

