What is the Matrix?
The matrix in mathematics is the rectangular range, arranged into columns and line numbers, symbols and expressions. The size of the matrix is 2 to 3 for example, since there are two rows and three columns: if they are of the same size, the element can be added to or subtract from two matrices.
ROW MATRIX
If a Matrix have only row then it’s called Row Matrix
[7 4 6] is a Row Matrix
[51 21 31] is a Row Matrix
COLUMN MATRIX
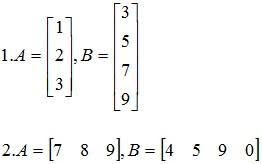
NULL MATRIX
Null Matrix is the matrix containing only 0 number.
I = [ ], P = [ ]
Check out also: BEARINGS
SPECIAL MATRIX
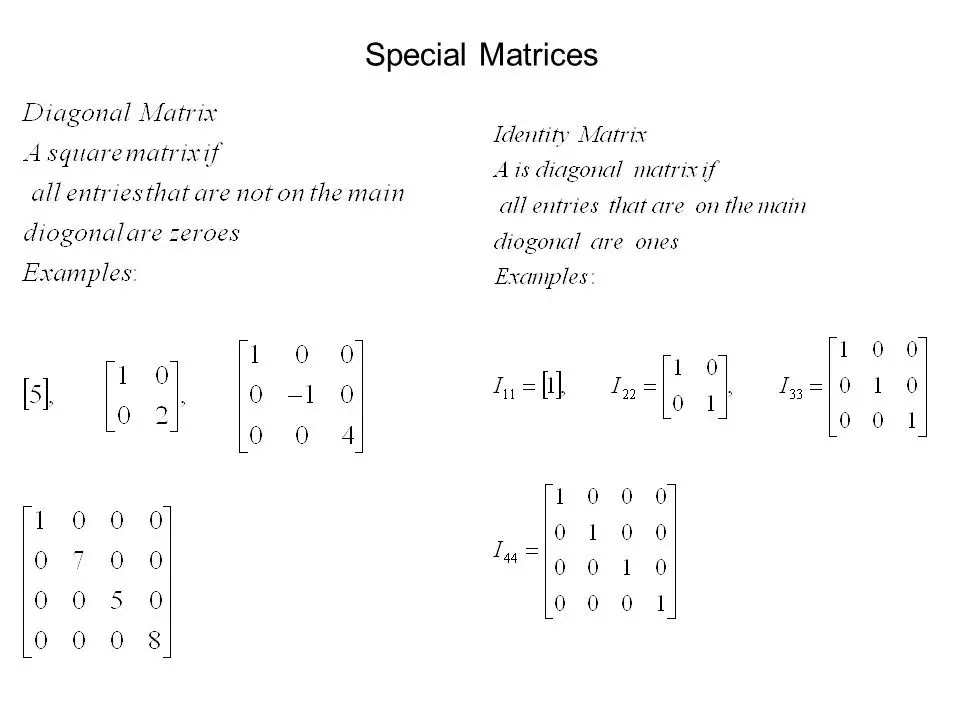
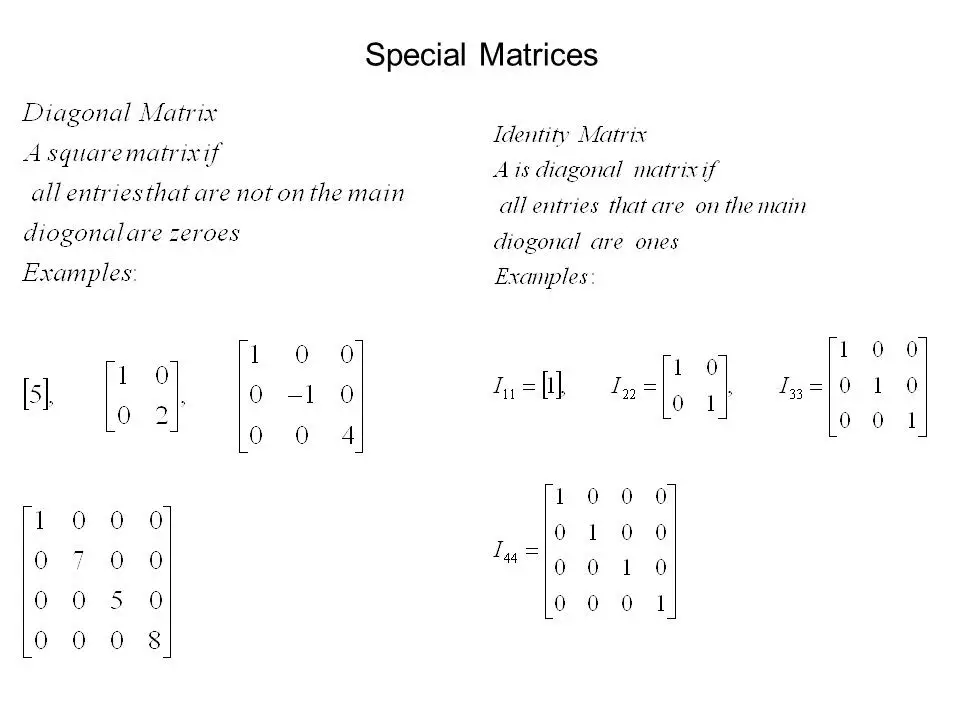
DIAGONAL MATRIX
Defined as a square matrix, where all zero elements from the top left diagonally to the bottom left.
IDENTITY OR UNIT MATRIX
The diagonal elements are just one’s.
ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF MATRICES
Matrices in the same order are added (or subtracted) by adding (or subtracting) the respective elements in each matrix.
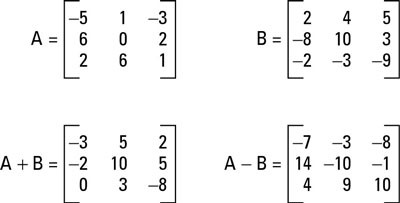
A+B = B+A: A and B will change location when added.
(A+B) + C = A + (B+C): order of operation bracket first.
Need Help? Ask Our Chat Assistant!
A – B ≠ B – A: A and B do not shift roles when subtracting.
Check out also: Mensuration
MULTIPLICATION OF MATRIX BY A REAL NUMBER
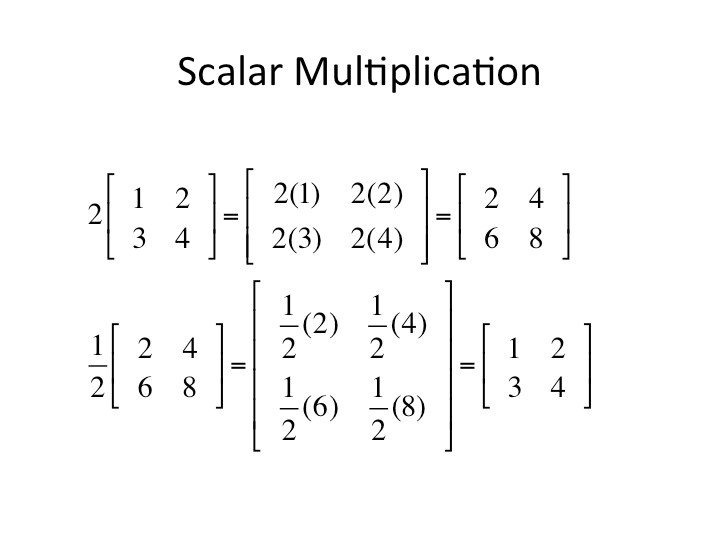
Matrices can only be multiplied only if they are compatible. They become consistent because the number of rows of the second matrix is the same as the number of columns of the first matrix.