SIN, COS, TAN:
Sine, cosine, and tangent are the most often known trigonometric functions. They are the cosecant, the secant and the cotangent, respectively, less common in modern mathematics.
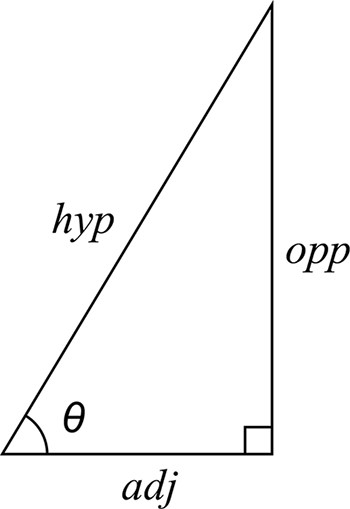
A right-angle triangle is a triangle with one side is a right angle. The longest hand, that is opposite the right angle, is the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle. The opposite hand is the line to the right side of the angle. The other side of the angle is opposite.
Check out also: Properties Of Circle
Formula:
The sine of the angle = the length of the opposite side
the length of the hypotenuse
The cosine of the angle = the length of the adjacent side
the length of the hypotenuse
The tangent of the angle = the length of the opposite side
the length of the adjacent side

Graphs of Sin, Cos, Tan:
The following examples show the Sin ø, Cos ø and tan ø values toward ø (ø is an angle). The graph of Sin ø = Sin ø 0 is visible if it’s = 0 °, 180-degree, 360 degree.
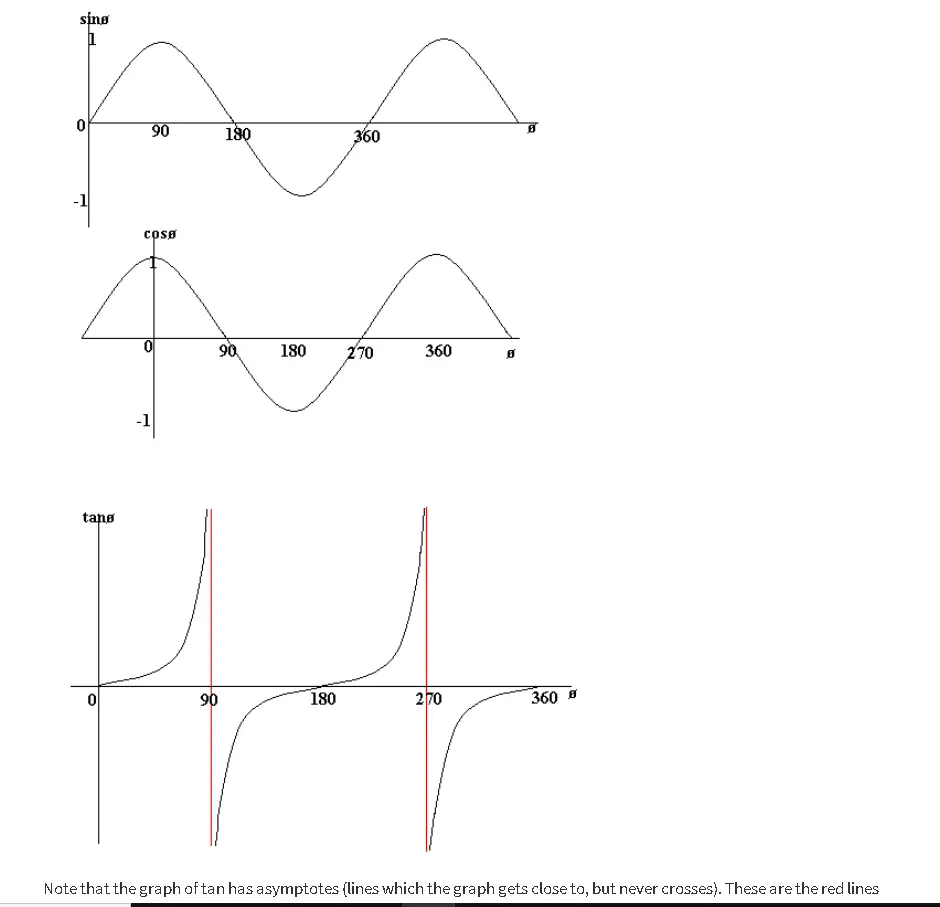
Note that the tan diagram has asymptotes (line that the diagram approaches but does not cross). Those are the red lines (which currently are not used in the graph).
Notice also that sin, cos and tan graphs are regular. That means you repeat yourself. For instance, sin(ø) = sin (360 + ø).
Please also note the graph symmetry. In a y-axis, for example, cos is symmetrical, meaning cos-ø = cos(-ø). So, cos (30) = cos (-30), for example.
In addition, the symmetry of sin in line ø = 90 makes sin x = sin (180-x).
Check out also: Vectors
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM:
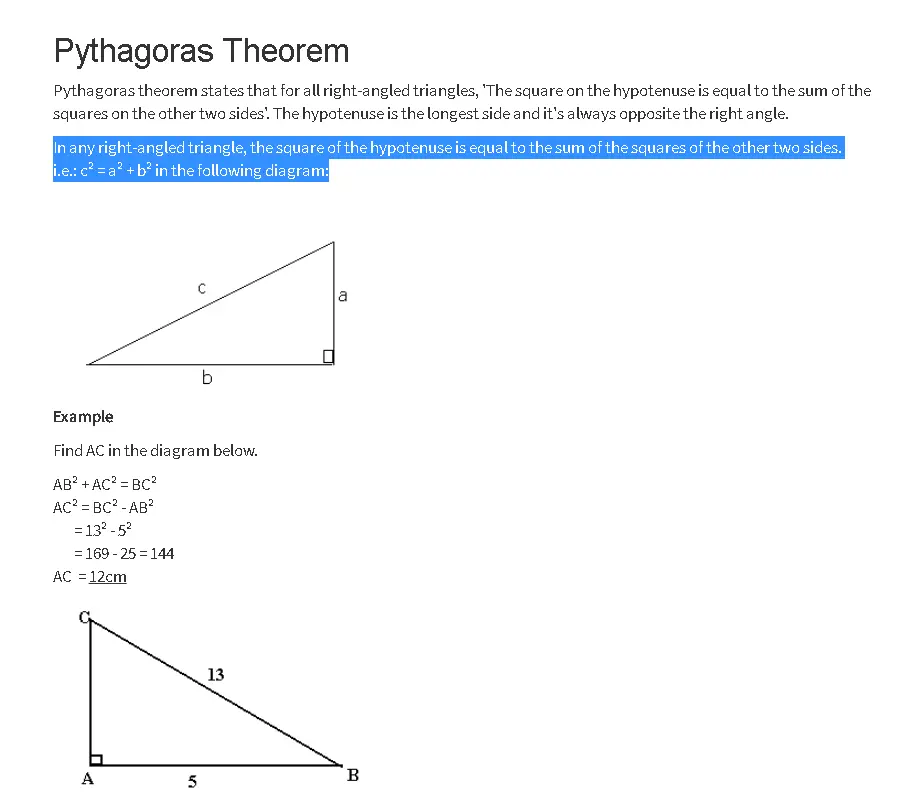
The theorem of Pythagoras is an important subject in mathematics which explains the relation among the sides of the right-angled triangle. It’s also called Pythagorean Theorem sometimes. Examples illustrate the formula and proof of this theorem. The definition of this equation is the right-angle triangle, from which the basis and perpendicular and hypogynous formula can be obtained.
The hypotenuse square is equivalent to the sum of the squares on the other two sides in every right- angle triangle.
For example:
c² = a² + b² in the following diagram:
Problem:
A cuboid has sides of length 10cm, 2 √11 cm and 5cm. Find the length of a diagonal.

So, we want to find AD.
We can draw a right-angled triangle inside the cuboid which has AD as it’s hypotenuse. Then we can use Pythagoras.
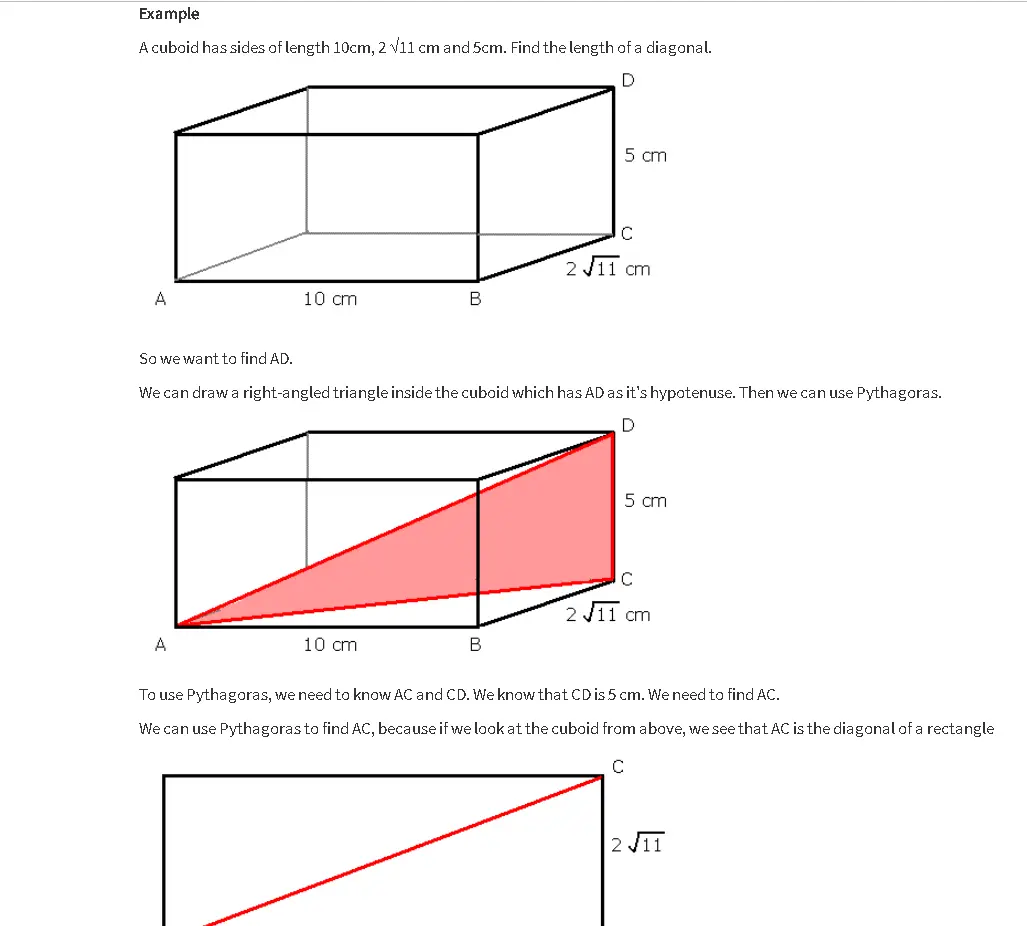
We need to learn AC and CD to use Pythagoras. CD is 5 cm; AC must be found.
We can use Pythagoras to find AC, since we can see that AC is the cuboid diagonal of the rectangle from above.
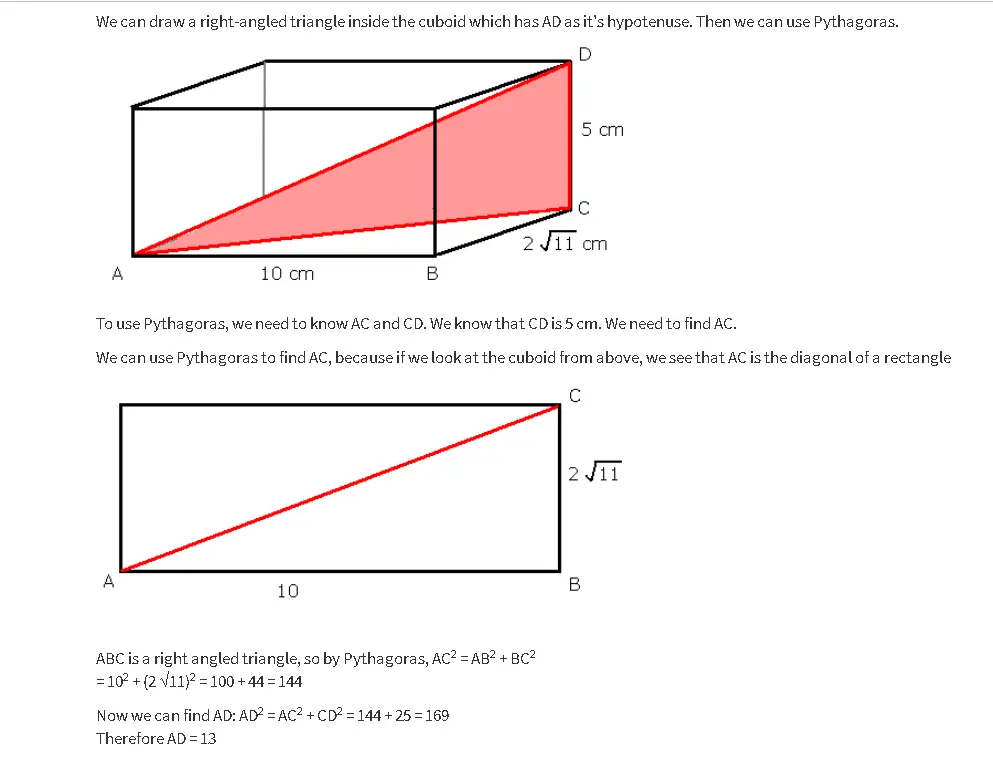
ABC is a right-angled triangle, so by Pythagoras, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
= 102 + (2 √11)2 = 100 + 44 = 144
Now we can find AD: AD2 = AC2 + CD2 = 144 + 25 = 169
Therefore AD = 13
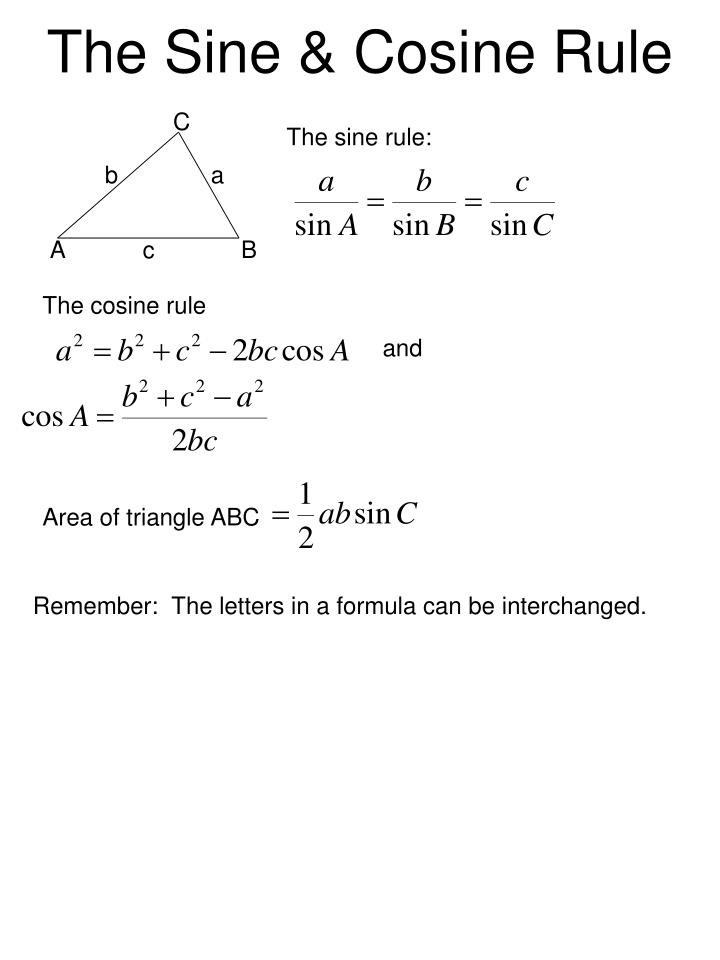
Sine and Cosine Rule:
CONGRUENCY:
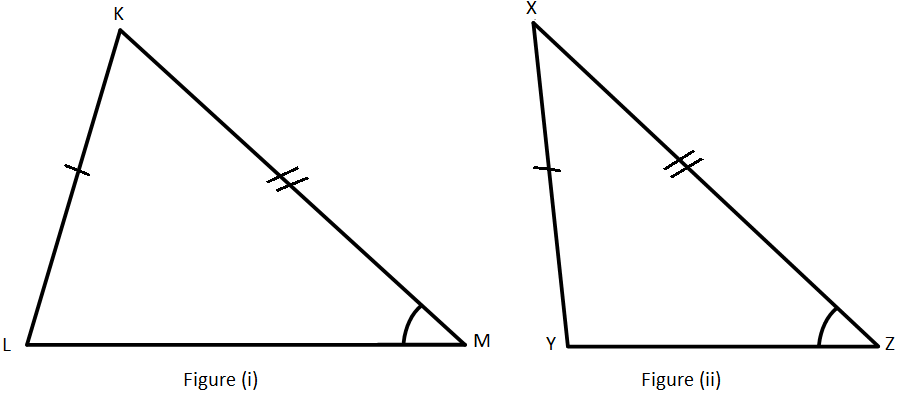
When they are similar (shape and size), two shapes are congruent; in other words, if the sides and the angles are equal. When two triangles are congruent, it is often useful to know.
If one of the following is real, two triangles are congruent:
- All of the three faces are the same length as the other triangle ‘s three faces (i.e. a = d, b = f and c = e) under it). We write “SSS” if you know this is real.
- Two angles and one side of the triangle are equal to the two angles corresponding to the other, e.g. A = D, C = E and a = d); We write “ASA” for this reason.
- The angle of the triangle between the two sides is equal to that of the other triangle, and the sides of the triangle are similar (e.g. C = E, b = f, a = d). We are writing ‘SAS’.
- The same hypotenuse has two right-angled triangles and one is identical to the other.
Congruency and Transformation:
If a process is transformed, rotated, or replicated, what lies behind us is aligned with what we began. That’s because a translation just shifts a form: the angles or the lengths of the sides do not change.
It’s the same as a rotation. A reflection could change the appearance of the shape, but the longitude of any side or the size of its angles does not change.

