849
ntent -->
Spread the love
Transmission of Data:
- The transfer of data in the form of bits from one device to another can be described.
- Some type of medium, for example, fiber optics, etc. is necessary to transmit data.
- The data can be transmitted from the machine to the printer over a short distance or long distances, for example calling abroad by telephone.
- For data transmission three key considerations must be considered:
- The path for data transfer (one or two way).
- Form of transmitting i.e. not one-time bits to pass.
- Form of syncing.
Types of Data Transmission:
There are two types of data transmission:
- Serial
- Parallel
Serial Data Transmission:
- In serial communication systems, there is a single wire over which data bits are transferred one by one.
- It is known as serial transmission because bits need to be organized before they are sent over the channel.
- This way the receiver can receive and arrange data in order and consider it to be errorless.
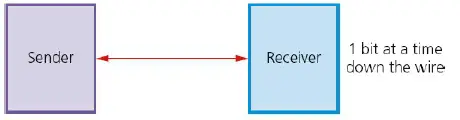
- This data processing is often used where long-distance connectivity is required.
- In serial communication systems, data transfer speed is slower than in parallel communication systems.
- There is no problem with synchronization when transmitting serial data.
Example:
An example of serial data transmission is the transfer of bits from the computer to the modem for transmission over the phone.
Parallel Data Transmission:
- Multiple wires in the concurrent transmission networks are transmitted continuously via these parallel wires.
- This data transmission method is the best practical application over shorter distances.
- The bit can be skewed when a long-distance synchronization issue is used.
- Used for internal communications usually in computer networks.
- It is faster than serial data transmission.
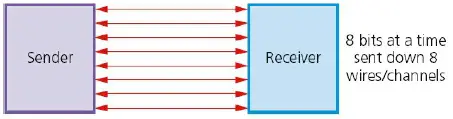
Example:
An example of parallel data transmission is a ribbon wire that is used to transfer data from the computer to the printer.
Modes of Data Transmission:
There are three modes of data transmission:
- Simplex
- Duplex
- Half-Duplex
Simplex Data Transmission:
In this mode, data is transmitted in one direction only i.e. sender to receiver.
Example:
Transfer of data from computer to printer.
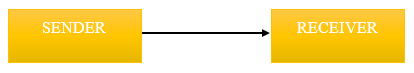
Duplex Data Transmission:
In this mode, data is transmitted in both directions simultaneously.
Example:
Broadband phone connection.
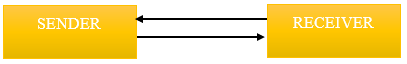
Half-Duplex Data Transmission:
In this mode, data is transmitted in both directions but not simultaneously i.e. not at the same time.
Example:
A phone conversation.
Error Detection & Correction in Data Transmission:
- The techniques used for data processing are known as error detection while the transmission of data, sound, and other impairments happen.
- Error identification allows efficient channel data distribution.
- It, therefore, decreases the risk of undetected error, i.e. the shift of inappropriate frames.
- An algorithm of some kind is added to the error detecting code normally transmitted on the channel by the data before transmission of the data.
- The receiver uses the same algorithm, produces the submitted data’s error code, and then compares it to the end-of-sending Error Code.
- If all codes are similar then the obtained data is error-free.
- The submitted information shall otherwise be deemed inaccurate and the applicant shall then take action.


