What Are Enzymes?
Enzymes are the chemical catalysts in protein. Chemical reactions accelerate from catalysts. The molecules on which enzymes work contain substrates and the substrates transform into products. The molecules are called substrates.
A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction; however, the reaction is not altered.
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a substance which, in case it is left at room temperature for a period of time, is broken down into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2).
That could be a long time, but if we add a catalyst, it might be speeded up. Every catalyst can and cannot catalyze a specific material. Manganese4 is the precursor for hydrogen peroxide.
When added, in very short time, water and oxygen gas are received and the oxide of manganese4 can be regenerated.
Read also: IGSCE Biology (0620)
How did it work?
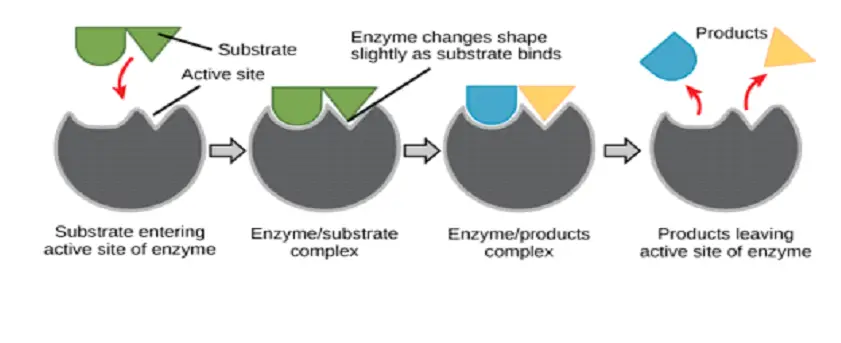
⦁ Enzymes are acting in the same manner as catalysts and can be used more than once using just one substrate.
⦁ Only one material can fit into the active place for digestion, and this enzyme works with only one substratum.
⦁ The way enzymes act like a key and a lock can be thought of, as the substrate is key and the lock is the enzyme.
⦁ The key should be the correct form to fit in the lock and the substratum to fit into the enzyme ‘s active place.
⦁ Enzymes of the constructors do the reverse to enzymes of the breaker.
Read also: A level Biology (9700)
Effect of Temperature on the enzyme’s activity:
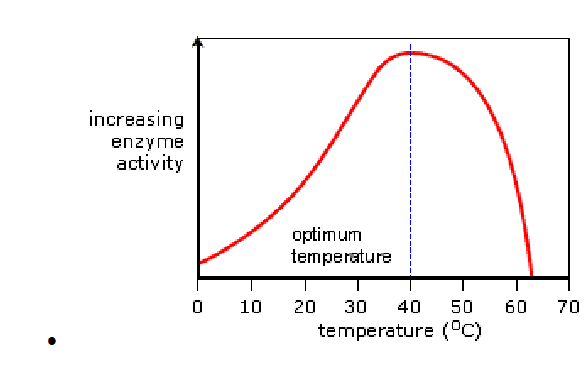
.The temperature at which the enzyme is most active is the best one at each enzyme, and below this temperature the enzyme activity decreases until it is inactive at low, above this optimal temperature the enzyme is denatured and can no longer function.
⦁ With the rising temperature, the enzyme and substrate are having more kinetic energy and colliding quicker, the enzyme becomes more active and the reaction occurs.
⦁ If the temperature reaches its optimum temperature, the enzyme will die and become denatured when the heat passes optimally.
The Effect of pH on the Enzymes activity:
The pH observations of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance or solution. As at temperature, enzymes have an optimum pH. The scale is between 1 and 14. pH 7 is neutral, it’s acidic below and alkaline above.
When this pH varies, the shape of the enzyme’s active site is changed and the substrate cannot adapt into this, and the enzyme is unsuccessful. Every enzyme has an optimal pH.
Read also: DRUGS
Use of Enzymes in Seeds Germination:
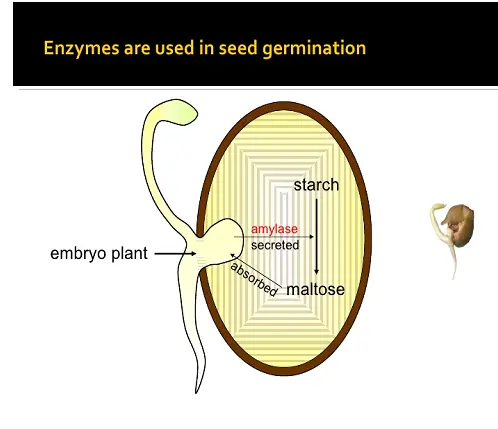
Seeds are germinated into plants. The gemmation of seeds involves the breaking of enzymes into the seed stored for use in cells of growth, energy, and construction.
⦁ Starch: Starch is divided into maltose with an amylase enzyme, then maltose’s is divided into glucose used in the breathing by maltase enzyme.
⦁ Proteins: Protein is divided into protease enzymes into amino acids; and amino acids are used in the formation of cells and growth.
⦁ Fats: Fats by lipase enzyme are classified into fatty acids, used to make cell membranes.
Some conditions must be present for a seed to germinate:
⦁ Water: Enzymes are activated.
⦁ Oxygen: Used for breathing.
⦁ Warm temperature: For optimum working and temperature conditions for the enzymes.

