What are Nutrients?
The nutrition inputs containing raw goods and tissue repair energy, absorbing and assimilating nutrients that are organic substances and mineral ions.
Meat is one of the living organisms’ characteristics.
All organisms do so, to obtain energy and raw materials necessary for growth and remediation for vital activities.
Depending on your age, size, sex, and activity, each individual must take a certain amount of every nutrient every day.
Seven resource forms exist, the following are:
⦁ Carbohydrates
⦁ Protein
⦁ Fats
⦁ Vitamins
⦁ Resources
⦁ Tumbling.
⦁ Water
CARBOHYDRATES
These organic substances are sugars, protein, fats, and vitamins. This means that living beings (plants) are formed and they are built-in carbon atoms.
Organic materials such as carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic minerals are produced by plants. This is not what animals can do.
Functions:
This is used as a reservoir of energy and is important for stress-free breathing. This is used to produce cellulose, a material that shapes plant cell walls.
⦁ Monosaccharides: the smallest and most common type
⦁ Soluble vapor
⦁ C6H12O6 compounds
⦁ For example, glucose-fructose-galactose.
⦁ Sources: Honey-Fruits
Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides joined together in each molecule each
⦁ Soluble vapor
⦁ Examples: Maltose’s-Lactose. Examples:
⦁ Sources: Sugar-Milk Table
Polysaccharides: Many single molecules from a long chain together with monosaccharides.
⦁ In water insoluble
⦁ Examples: Glycogen cellulose-starch.
⦁ Sources: Bread-potatoes pasta, plant cell cellulose, and levier glycogen.
Protein
These include the sugars, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and, rarely, phosphorus or sulfur components.
A protein molecule is a long chain of simpler units known as amino acids.
Fat
The filter paper analysis or an alcohol test is used to test its effect. A flat spot can be seen whether fats occur using the experiment with filter paper.
Photosynthesis:
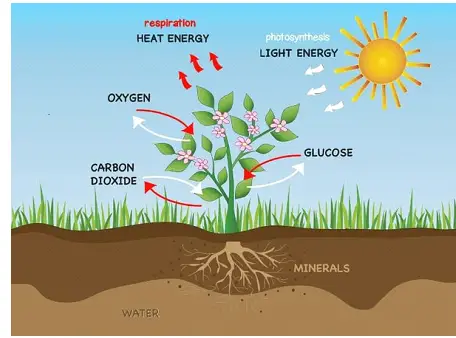
Photosynthesis, which converts light energy into chemical energy, in green plants, and many other organisms. During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is absorbed and converted to oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds by soil, carbon dioxide, and minerals.
The requirement for photosynthesizing chlorophyll, light, and carbon dioxide:
⦁ Chlorophyll is important because it helps to absorb the needed “light.”
CO2, when converted into sugars like glucose we use, is essential. CO2.
⦁ Light is critical as it acts as the fuel or power for the reaction
Factors that impact photosynthesis rates:
⦁ Intensity of light
⦁ The concentration of carbon dioxide
⦁ Temperature
The Process of Photosynthesis:
⦁ Water is drained into the water channels of the veins and removed from the soil by the roots of plant plants.
⦁ Carbon dioxide (pores in the leaf) is absorbed from the soil by the stomach.
⦁ CO2 and H2O are used for the processing of sugar in the leaf cells.
⦁ Sunlight ingested by green pigments chlorophyll has provided the catalyst for this reaction.
⦁ Chlorophyll can capture energy from light and use it in hydrogen and oxygen separating water molecules.
⦁ Within the molecules of carbon dioxide, the oxygen leaves, and the hydrogen ions are added to form sugar.
⦁ The light energy was then converted in a synthesized manner to the chemical energy of carbohydrates.
Limiting Factor:
⦁ It is present in the environment in such short supply that it limits life processes.
⦁ Although the concentration of carbon dioxide limits photosynthesis only directly, artificially high levels of carbon dioxide
in greenhouses effectively increase crop yields.
⦁ Greenhouses also maintain higher temperatures, thus reducing the effect of low temperatures as a limiting factor and optimizing the light reaching the plant.
⦁ Parts of the world, such as tropical countries, often enjoy optimum temperatures and rainfall for crop production.
⦁ The stomata in the leaf may affect the rate of photosynthesis depending on whether the leaf is open or closed.
Compensation Point:
Effect of the gas exchange of the aquatic plant kept in the dark and light:
The hydrogen carbonate indicator is used to show the concentration of carbon dioxide in the solution. It is as follows:
⦁ Yellow at high carbon dioxide concentrations
⦁ Red in balance with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
⦁ Purple at low carbon dioxide concentrations
Place a plant leaf in a stoppered boiling tube containing a hydrogen carbonate indicator.
The effect of light can then be investigated for a few hours.
Plant cells respire in the dark and light, releasing carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis can also occur in the light, and carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air. If the light is bright enough, the absorption rate will be higher than the release rate.
Leaf Structure:
⦁ Mid-rib: contains xylem and phloem.
⦁ Vein: contains xylem and phloem.
⦁ Lamina: the photosynthesis site and the production of useful substances.
⦁ Cuticle: Made of wax, waterproofing of the leaf. It is secreted by the upper epidermis cells.
⦁ Upper epidermis: These cells are thin and transparent to allow light to pass through. There are no chloroplasts present.
They act as a barrier to disease.
⦁ Palisade Mesophyll: a layer of palisade cells that carry out most of the photosynthesis
⦁ Spongy Mesophyll: a layer of spongy cells below the palisade layer, they perform photosynthesis and store nutrients.
A healthy diet consists of all food classes in the right proportions.
The food groups needed are:
⦁ Carbohydrate
⦁ Protein
⦁ Lipids
⦁ Vitamins
⦁ Minerals
⦁ Dietary fabric
⦁ Heat.
OMNIVORES: consume food of animal and plant origin. Yeah, cows, the bears, the wild boars, and the chickens are omnivorous. Humans Beings, too, are omnivores.
CARNIVORES: consume other species, eagles, bears, lions, etc.
HERBIVORES: are chewing food. Deer, bunny, and grasshopper.
SCAVENGERSv is a form of carnivores. They ‘re fed on corpses, the fish, the snakes, are carnivores. They ‘re herbivores. Animals Vultures, hyenas, and a few beetles are scavengers. It’s an insect that consumes the bodies of dead creatures.
DECOMPOSES: feed on rotting plants and animals It’s time. All bugs, earthworms, spores, and molds This decomposes. It’s a living being that breaks down the waste of the farm and the water Remains of living organisms in fluids that are added to the ground

