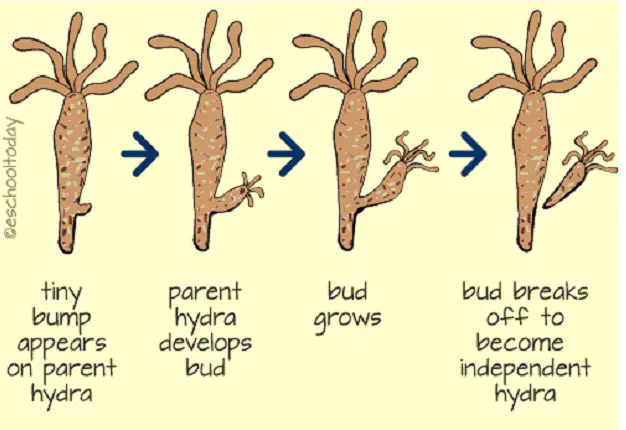
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Asexual reproduction is a reproductive form that does not require gametes fusion or changes in the number of chromosomes.
The offspring of a single cell or a multicellular organism, as an asexual development, inherits the parent’s genes.
BACTERIA:
⦁ Large single-cell organisms are bacteria. Through a mechanism called binary fission, they replicate.
⦁ Binary fission creates two identical copies of the genetically engineered DNA chain. The bacterium separates the parent and the sibling bacterium, where one DNA coil is separated.
⦁ Once every 20 minutes, each bacterium will undergo binary fission to reproduce huge numbers from one parent in very little time.
FUNGI:
⦁ Fungi are multicellular species that grow long strings on foodstuffs called hyphae.
⦁ The reproductive and feeding hyphae are two styles.
⦁ Reproductive hyphae develop above the food material vertically. There’s a spherical container at the end of the hyphae, which holds several spores.
⦁ The bag is known as sporangium. In sporangia, spores are reproductive constructs that can be converted into certain funguses. The sporangium will at some stage break open and disperse the spores in the air.
Once a spore falls into an environment of good conditions (food, water, and air), it grows and produces a new similar fungus.
Runners and rhizomes (stolon’s):
⦁ Some plants grow side branches automatically with seedlings.
⦁ It is the case for the spider to rose. Many plants, including strawberries, are producing runners and seedlings.
⦁ Under the sheet, Rhizome grows
Bulbs: Bulbs:
Naturally, certain plants grow underground organ storage that then becomes the plants of the next year – this is exemplified by potato tubers and daffodil bulbs.
Plant artificial cloning:
Cloning plants have many significant economic consequences: in a brief amount of time and on an immense scale, a good variety of a plant is produced cheaply
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| · This reproductive process requires vast quantities of offspring to be produced.
· All you have to do is place a specific organism in suitable habitat so that more new species will easily replicate.
· You can replicate life in only one place through asexual reproduction and you do not need to move anywhere just to see the process occurring.
· Remember that many plants and animals can rarely travel to other places will produce offspring alone.
· It can be incredibly difficult to find a mate, particularly to species in barren environments such as deep ocean habitats. |
· Because the features and traits of only one parent were passed on to its offspring, asexual reproduction will impede genetic variation all over its generations.
· Most of the time, it will still take a single asexual parent from which we would replicate chromosomes and DNA, which ensures the genetic abnormalities or anomalies that are carried out of asexual reproduction will always occur in the offspring without any exception.
· Such a disadvantage would also lead to more undesirable mutations, which make asexually created species resistant to infections, which often means a large amount of offspring can be lost.
· Many of the same attributes and features often include all of the same weaknesses, and we can conclude that a certain parasite or predator that has adapted to kill a single asexual organism would be able to wipe out its entire population. · In basic terms, asexual reproduction will lead to a struggle for life. |
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
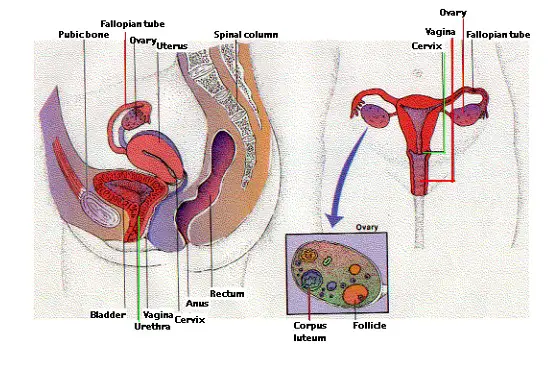
Sexual reproduction is a reproduction that requires a complicated life cycle in which a gamete with an individual set of chromosomes joins with a separate organism to create a cell with two chromosome sets.
⦁ The fusion of gamete nuclei is the fertilization. The male organs are composed of gametes.
⦁ The cell division process that makes the gametes is referred to as meiosis.
⦁ Throughout human reproduction, males and women unite, merge to create a new cell called a zygote. In other words, their cell cytoplasm to nuclei joins together.
⦁ The male gametes can be found in flowering plants in pollen grains and the female gametes classified as ovules as egg cells.
⦁ In mammals, sperm is male gametes and gametes are female eggs.
⦁ The male gamete is elastic and microscopic. The sperm bathes to the ovum and the pollen cell drives the pollen tube down.
⦁ The female gametes are often bigger and not male.
Chromosome Number:
⦁ Chromosomes are found in pairs of human body cells (somatic cells).
⦁ Human beings have 46 pairs of chromosomes. This is referred to as diploid
⦁ The number of chromosomes in the nucleus of each sex cell is decreased by half when the gametes are produced. That’s the trick.
⦁ When the nuclei of the sex cells fuse during fertilization, a zygote is formed.
⦁ The chromosomes are obtained from both gametes so that the cell is diploid.
Cross Breeding:
⦁ Biologists can use their genetic knowledge to produce a new plant and animal variants.
⦁ The lack of diversity is a long-term downside to selective breeding since certain genes are lost to species by removing all offspring that do not have the desirable characteristics.
⦁ Some of the potentially useful genes may no longer be available when new combinations of genes are sought.

