What are Organisms?
Too small to be observed by the naked eye, but visible through a microscope, is living organisms (such as bacteria, fungi, viruses). So, it is recognized as a microbe.
BACTERIA
The cells of bacteria are very different from all the other species’ cells since they have no nucleus. There may be photosynthesis in some bacteria.
This world contains the earliest fossils, and we conclude that they are the first forms of life to exist on earth.
BACTERIA IN DECOMPOSITION
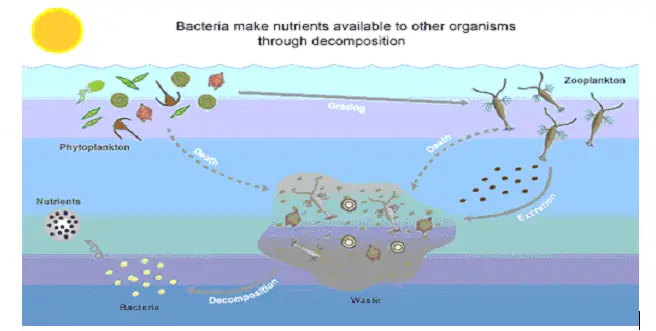
Saprophytes are one of the bacteria. They feed on organic matter that declines dead. Digestive enzymes are secreted from dead organic matter.
Carbohydrates are converted into glucose by enzymes, which are processed into the bacterial cytoplasm. During respiration, glucose is broken down to emit steam. In respiration, the carbon dioxide produced is used for photosynthesis by plants.
Around the same time, the same bacteria that are further converted into nitrogen by nitrifying bacteria break down nitrogenic compounds from dead species into Ammonia. Plants synthesize proteins from these nitrates.
It helps decomposition and recovers mineral nutrients.
Read also: ENZYMES
FUNGI
Fungi do not have chlorophyll and do not photosynthesize. They feed saprophytically, or parasitically, on organic material like faces, human foods, and dead plants or animals.
Fungi grow specialized areas for reproduction called fruiting bodies.
These can grow very large and be visible to the naked eye.
BIOTECHNOLOGY
Biotechnology is the method to use organisms and systems in the production and service industries in biological processes.
For example:⦁ Make of cheese
⦁ Production of yogurt
⦁ Bread
⦁ Producing antibiotics
⦁ production of alcohol.
⦁ Development of single-cell protein
PENICILLIN PRODUCTION
Penicillin is a secondary metabolite of certain Penicillium species and is formed by stress inhibition of fungal growth. There was a misunderstanding.
Especially essential are accessible carbon sources: glucose prevents the development of penicillin, while lactose does not.
The following steps are involved in the synthesis of Penicillin:
⦁ A wide tub called the Fermenter or Bioreactor holds an antibiotic penicillin id.
⦁ Fulfill the fermenter by nutrient broth, such as maize steep liquor (cultur media).
⦁ Carbohydrate lactose in the Nutrient Broth is used as an energy source, and protein-synthesizing amino acids.
⦁ The fermenter and the container are sterilized to kill any food-contaminating microorganisms.
⦁ Add additional necessary mineral ions.
⦁ pH about 5-6 is preserved
⦁ Temperature is held between 26 and 30oC.
⦁ For fungal aerobic respiration, sterilized air is injected into the fermenter.
Read also: A level Biology (9700)
SINGLE CELL PRODUCTION
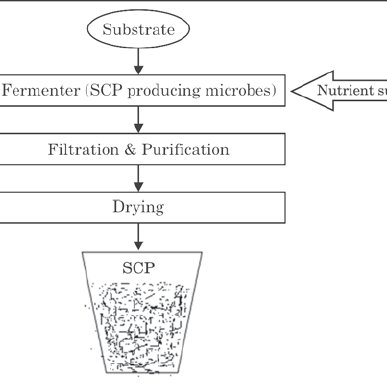
The protein produced by unicellular organisms is the single-cell protein. Protein is the main ingredient of the bacterial and fungal cytoplasm.
The bacterial protein is called protein and used as feed for livestock. The fungal protein is known as mycoprotein used as a food for human beings.
In a wide container called the Fermenter or Bioreactor, the single-cell protein is produced. The fungi may be used for growing the material such as molasses, liquid whey, etc.
In order to destroy the other microbes that contaminate the drug, the ferments and medium are sterilized.
The initial culture of Fusarium fungus is reactivated and added to the medium.
Inoculation is called this. Glucose as a source of carbon, ammonium or nitrate or as a nitrogen supply must be used in the process.
For fungal aerobic breathing, air is allowed in the medium.
The minimum pH shall be between 6 and 7 and the minimum shall be 27 to 30oC. The fermenter paddles spin to prevent fungal filaments from being obstructed.
Under these conditions the fungus multiplies in great numbers that are extracted from the fermenter, washed and used as foodstuff rich in proteins.
Read also: Cost, Revenue And Profit

