Methods of purification
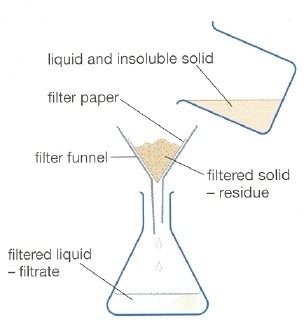
Filtration: Filtration is a physical, biological, or chemical mechanism that distinguishes solid and fluid from a combination of a filter medium that has a complicated structure in which the fluid is the only one capable of moving.
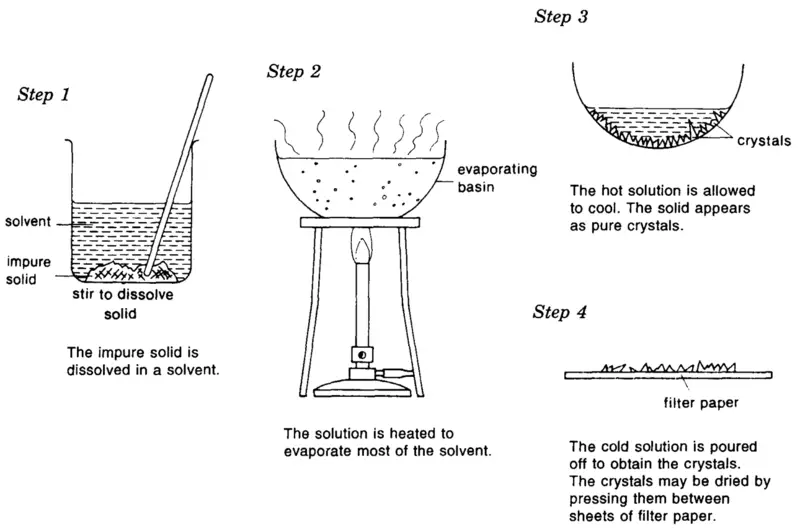
Crystallization: Crystallization is the mechanism by which a stable shape takes place, through which atoms or molecules are arranged into a structure called a crystal.
Any forms that the shape of crystals precipitate a solution, freeze it or deposition from gas more rarely.
Read also: Preparation of Salts
Concept of Separation:
The smallest classes of matter including electrons, molecules and minute particles are isolated.
These processes begin with a mixed-state sample and transform it into new samples, which – preferably – consist of one material.
Separation methods may also be characterized as processes modifying the relative quantities of substances within a mixture.
One may start with an entirely standardized or heterogeneous mixture of chemicals; certain particles are either partially or completely extracted from the sample during the separating process.
Distillation:
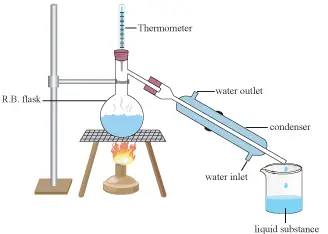
Distillation is a common process used to isolate mixtures depending on the variations in conditions required to change the mixture product phase.
The fuel may be heated to cause elements that have various boiling points in the gas phase in order to isolate a liquid mixture.
The gas is then reshaped and deposited in liquid form. Dual distillation is also repeating the cycle of the extracted material to improve solvent purity.
The reverse cycle may be used for the isolation of gasses by liquefying materials by adjusting temperature and/or pressure is the term most widely used for fluids.
Fractional:

Fractional distillation is a mechanism by which components are separated into different sections of a chemical mixture (called fractions). Fractional distillation for the purification of natural materials and the isolation of components in mixtures.
Example: Gasoline is made with a fractional distillation and several other chemicals from crude oil. Before it evaporates, crude oil is hot.
Under such temperature ranges, different fractions condense. Chemicals are hydrocarbons with equal amounts of carbon atoms in a given proportion.
The percentages from hot to cold (main hydrocarbons to smallest ones), fuel oil, gasoline, kerosene, naphtha, petrol and industrial gas may be residual.
Read also: Periodic Table & Group Trends
Using a suitable solvent:
| Solvent | It dissolves |
| Water | see “Soluble salt”, sugar |
| white spirit | gloss paint |
| propanone | grease, nail polish |
| ethanol | glues, printing inks, scented substances in perfumes and aftershaves |
Choosing a suitable separation method:
| Method of separation | Used to separate |
| filter | a solid from a liquid |
| evaporate | a solid from a solution |
| crystallize | a solid from a solution |
| Distil | a solvent from a solution |
| fractional distillation | liquids from each other |
| chromatography | different substances from a solution |