Elements:
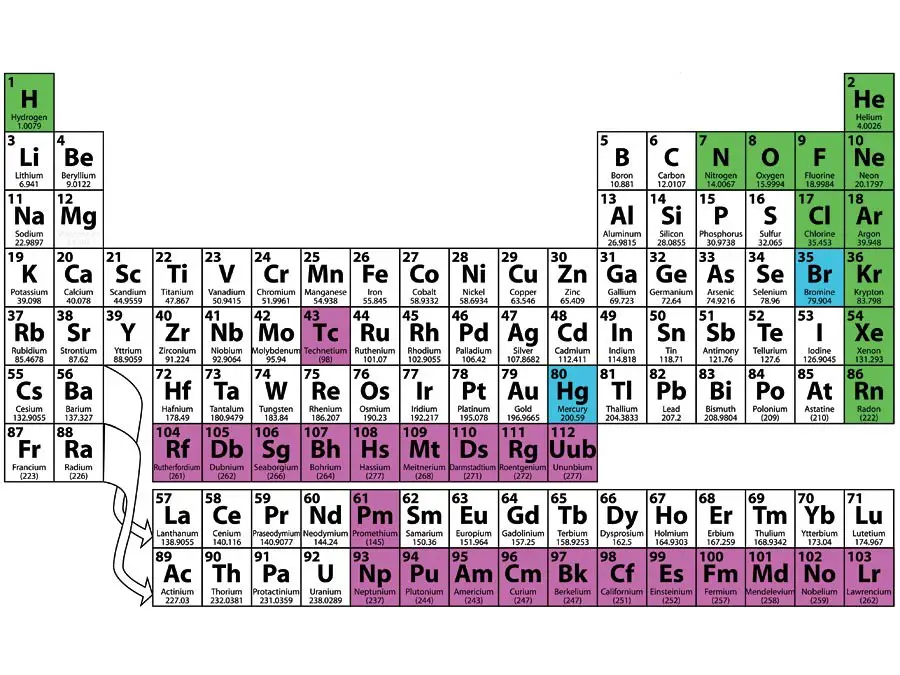
An element is a material that cannot be separated into another. There are approximately 100 elements of their atom form. The atoms of at least one or more elements hold everything of the universe.
The periodical table summarizes all known elements and groups them together with similar characteristics.
Many of the elements are light metals that conduct electricity well. Gold, aluminum, and iron all contain solid metals at room temperature. The single fluid metal at room temperature is Mercury.
Read also: ELECTROLYSIS
Atoms:
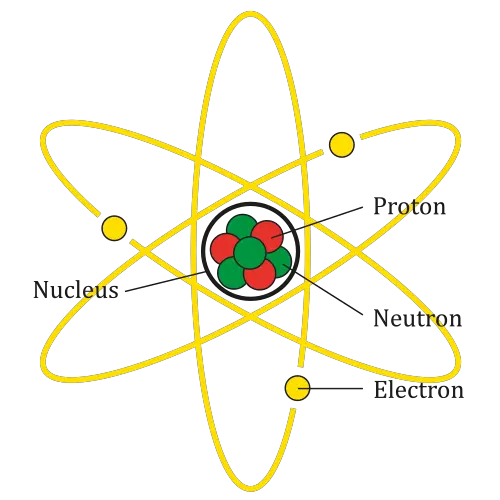
Three fundamental particles are made up of atoms: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The atomic nucleus (center) comprises the protons and neutrons (positive loads) (no loads).
Electron shells hold the electrons (negative charged) which are the outermost regions of the atom. Atoms have various properties depending on their shape and number of simple particles.
Electron:
Electrons weighing around 10 to 28 grams per individual or around 1:1800 of an atomic mass unit are significantly lighter in weight than protons.
They also don’t play a part in the total atomic mass of an element. In respect of atomic mass, the mass of all electrons is generally neglected and the mass of the atom is determined based on the sum of protons and neutrons alone.
Electrons make a large difference to the atomic charge since an electron has a negative load equal to a proton positive load.
Proton:
Protons and neutrons have about the same weight, about 1,67 x 10-24 grams. This sum is known as a single atomic mass unit (amu) or a Dalton by scientists.
While protons are positive in mass, the subatomic particles charged are positively charged and form part of an atom’s nucleus and decide the atomic number of an item. This is 1 amu in weight.
Neutron:
Neutrons are not released in natural, nuclear decline cases, so neutrons can no longer be expedited by machines because electrons so nuclei are electrically neutral particles.
But in the accelerator beams, neutrons can be produced through nuclear reactions initiated by high-energy particles. Once bombarded by high-speed particles several target materials yield neutrons.
Need Help? Ask Our Chat Assistant!
Compound
A pure material that consists of more than one element from chemically related.
Set elements bond, and hence the chemical structure can be portrayed. Since sodium chloride, for example, contains as many sodium ions as chloride ions, the formula is NaCl, whereas water is still half as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen and its H2O.
Read also: CHEMICAL BONDING
For example:
Table salt or sodium chloride (NaCl, an ionic compound), sucrase (molecule), nitrogen gas (N2, molecule covalent), copper sample (intermetallic), water, and H2O (covalent molecule), among other compounds.
Mixture
An impure substance made from different elements or compounds mixed that are not chemically joined.
Mixtures can usually be separated by physical techniques such as filtering and distillation.
Air is a mixture that contains the elements nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and also the compound carbon dioxide.
Differences Between them
Differentiating Properties |
Compounds |
Mixtures |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Definition
|
The compound is a material that can be formed by adding two or more elements chemically. | Mixtures are compounds created by combining two or more substances physically. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Types | There can be three different types of compounds, i.e.: covalent, metallic, or ionic compounds.
The compounds can be categorized according to the carbon content in the molecular structure as organic compounds or as inorganic compounds. |
Mixtures consist primarily of two kinds of mixtures, i.e. homogeneous and heterogeneous. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substance Category | Pure substances are the target of compounds | Mixtures may be marked as impurities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composition | Compounds are often set in the chemical composition. | The composition of the compounds that make up a mixture is variable. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nature | Compounds are often fixed in the chemical composition. | A combination of the substances that create it may have a variable composition. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Properties | The properties of the compounds are special and do not inherently reflect the properties of the materials. | The elements of a mixture do not lack their characteristics and thus the characteristics of a mixture are usually the sum of their properties. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New Substance | When chemical compounds are mixed, new material is produced. A compound thus has different characteristics than its elements. | The mixtures don’t shape new substances and the characteristics are dependent on their properties. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting Point | A compound is also determined by its melting & boiling points. | A mixture does not describe the mixing and boiling points. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example | Alcohol, Wa
Elements:An element is a material that cannot be separated into another. There are approximately 100 elements of their atom form. The atoms of at least one or more elements hold everything of the universe. The periodical table summarizes all known elements and groups them together with similar characteristics. Many of the elements are light metals that conduct electricity well. Gold, aluminum, and iron all contain solid metals at room temperature. The single fluid metal at room temperature is Mercury.
Atoms:Three fundamental particles are made up of atoms: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The atomic nucleus (center) comprises the protons and neutrons (positive loads) (no loads). Electron shells hold the electrons (negative charged) which are the outermost regions of the atom. Atoms have various properties depending on their shape and number of simple particles. Electron:Electrons weighing around 10 to 28 grams per individual or around 1:1800 of an atomic mass unit are significantly lighter in weight than protons. They also don’t play a part in the total atomic mass of an element. In respect of atomic mass, the mass of all electrons is generally neglected and the mass of the atom is determined based on the sum of protons and neutrons alone. Electrons make a large difference to the atomic charge since an electron has a negative load equal to a proton positive load. Proton:Protons and neutrons have about the same weight, about 1,67 x 10-24 grams. This sum is known as a single atomic mass unit (amu) or a Dalton by scientists. While protons are positive in mass, the subatomic particles charged are positively charged and form part of an atom’s nucleus and decide the atomic number of an item. This is 1 amu in weight. Neutron:Neutrons are not released in natural, nuclear decline cases, so neutrons can no longer be expedited by machines because electrons so nuclei are electrically neutral particles. But in the accelerator beams, neutrons can be produced through nuclear reactions initiated by high-energy particles. Once bombarded by high-speed particles several target materials yield neutrons. Compound A pure material that consists of more than one element from chemically related. Set elements bond, and hence the chemical structure can be portrayed. Since sodium chloride, for example, contains as many sodium ions as chloride ions, the formula is NaCl, whereas water is still half as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen and its H2O. For example: Table salt or sodium chloride (NaCl, an ionic compound), sucrase (molecule), nitrogen gas (N2, molecule covalent), copper sample (intermetallic), water, and H2O (covalent molecule), among other compounds. Mixture An impure substance made from different elements or compounds mixed that are not chemically joined. Mixtures can usually be separated by physical techniques such as filtering and distillation. Air is a mixture that contains the elements nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and also the compound carbon dioxide. Differences Between them
ter, etc. |
Sand, water and sand and iron filings mixture, water and oil mixes, salad portion, train mixture, and concrete (not cement).
Elements:An element is a material that cannot be separated into another. There are approximately 100 elements of their atom form. The atoms of at least one or more elements hold everything of the universe. The periodical table summarizes all known elements and groups them together with similar characteristics. Many of the elements are light metals that conduct electricity well. Gold, aluminum, and iron all contain solid metals at room temperature. The single fluid metal at room temperature is Mercury.
Atoms:Three fundamental particles are made up of atoms: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The atomic nucleus (center) comprises the protons and neutrons (positive loads) (no loads). Electron shells hold the electrons (negative charged) which are the outermost regions of the atom. Atoms have various properties depending on their shape and number of simple particles. Electron:Electrons weighing around 10 to 28 grams per individual or around 1:1800 of an atomic mass unit are significantly lighter in weight than protons. They also don’t play a part in the total atomic mass of an element. In respect of atomic mass, the mass of all electrons is generally neglected and the mass of the atom is determined based on the sum of protons and neutrons alone. Electrons make a large difference to the atomic charge since an electron has a negative load equal to a proton positive load. Proton:Protons and neutrons have about the same weight, about 1,67 x 10-24 grams. This sum is known as a single atomic mass unit (amu) or a Dalton by scientists. While protons are positive in mass, the subatomic particles charged are positively charged and form part of an atom’s nucleus and decide the atomic number of an item. This is 1 amu in weight. Neutron:Neutrons are not released in natural, nuclear decline cases, so neutrons can no longer be expedited by machines because electrons so nuclei are electrically neutral particles. But in the accelerator beams, neutrons can be produced through nuclear reactions initiated by high-energy particles. Once bombarded by high-speed particles several target materials yield neutrons. Compound A pure material that consists of more than one element from chemically related. Set elements bond, and hence the chemical structure can be portrayed. Since sodium chloride, for example, contains as many sodium ions as chloride ions, the formula is NaCl, whereas water is still half as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen and its H2O. For example: Table salt or sodium chloride (NaCl, an ionic compound), sucrase (molecule), nitrogen gas (N2, molecule covalent), copper sample (intermetallic), water, and H2O (covalent molecule), among other compounds. Mixture An impure substance made from different elements or compounds mixed that are not chemically joined. Mixtures can usually be separated by physical techniques such as filtering and distillation. Air is a mixture that contains the elements nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and also the compound carbon dioxide. Differences Between them
|