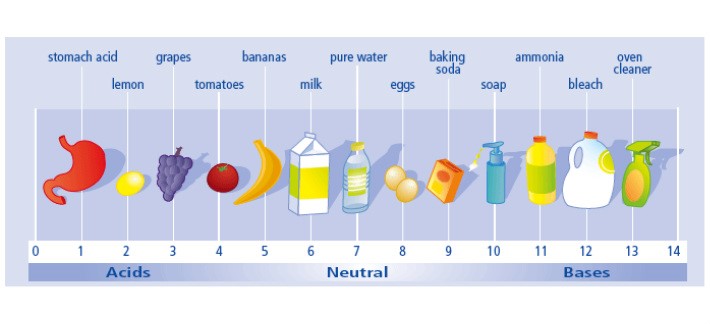
What are acids?
An acid is a chemical species that gives or receives protons or hydrogen ions. Many of the acids contain a hydrogen atom connected to which cation and anion in water are released (dissociated).
More acid-produced hydrogen ion concentrations, more acidity, and pH of the solution are higher.
All acids contain hydrogen ions, but not all compounds that contain hydrogen are acids, e.g. NH3. This is because NH3 does not produce hydrogen ions in water.
It is the hydrogen ions produced that are responsible for the properties of acids.
Properties of Acids:
- sour -flavored acids.
- They have a pH of less than 7.
- In general, they are in nature corrosive. As the pH is lower, the more corrosive it is.
- Change into Blue litmus red paper.
- Dissolve into the water to form electricity-driven solutions.
- Acids react to hydrogen and salt using reactive metals. Salt + hydrogen-> metal + acid
- Acids react to salt, carbon dioxide, and water with carbonate. Carbonate + acid-> salt + CO2 + water.
- Acids lead to the forming of salt and water by metal oxides and hydroxides. Oxide metal + acid-> hydrogen + salt.
Acids only show the properties of acids when they are dissolved in water. This is because acids dissociate in water to produce the hydrogen ions which are responsible for the acidic properties.
Read also: Balancing Chemical Equations
BASES
A base is any metal oxide or hydroxide. This means that a base contains either oxide ions O2- or hydroxide ions OH–.
We can also define a base as a substance that reacts with an acid to give a salt and water only.
base + acid -> salt + water
For example,
CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) -> CuSO4 (aq) + H2O (l)
In this case, copper (II) sulphate CuSO4 is the salt produced.
Example 2
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) -> NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
In this case, sodium chloride NaCl is the salt produced.
Note in the above cases, the oxide ions or the hydroxide ions from the bases react with the hydrogen ions from the acids to form water. This reaction is known as neutralization, and it is represented by the ionic equation below.
OH– (aq) + H+ (aq) -> H2O (l)
It occurs between alkalis and acids.
Alkalis:
An alkali is a water-soluble base. An alkali produces hydroxide ions OH – in an aqueous solution.
Many foundations of water are insoluble. They’re not known as alkalis. Alkaline sources include the NaOH, potassium hydroxide KOH, the Ca (OH)2 calcium hydroxide, and NH3 acoustic ammonia in some situations.
Properties of Alkalis:
- Alkalis have a bitter taste and a soapy feel.
- They have a pH above 7.
- The higher the PH, the more corrosive they are.
- They turn red litmus paper blue.
- All alkalis produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
- All alkalis can react with water to form salt and water only. This is known as neutralization. We have already discussed this.
- Alkalis heated with ammonia salts give off an ammonia gas. alkali + ammonium salt -> ammonia + salt + water
- Alkalis can react with a solution of one metal salt to give a metal hydroxide and another metal salt. alkali + salt (of metal A) -> metal hydroxide + salt (of metal B)
Uses of Acids:
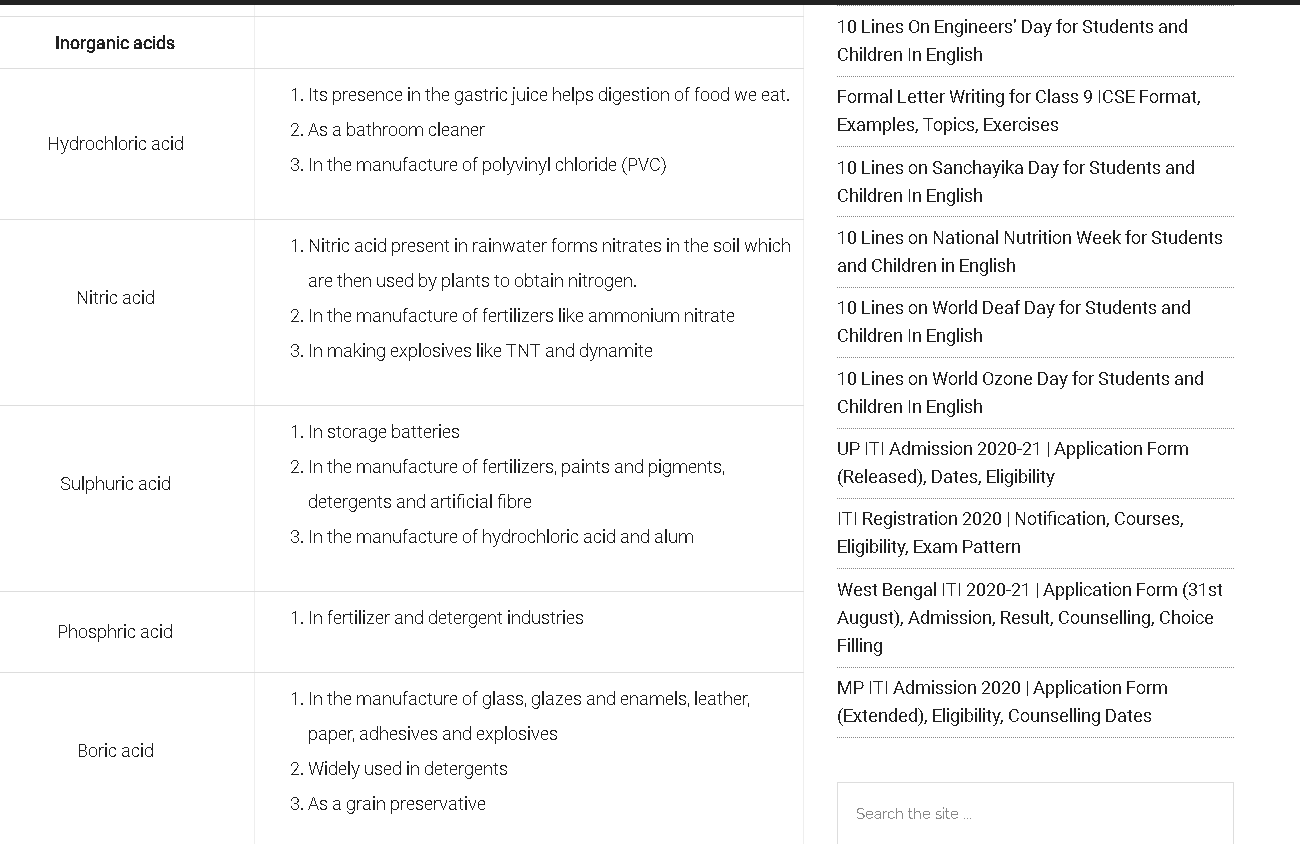
Read also: CHEMICAL BONDING
Uses of Bases:
- Soap and paper are made using sodium hydroxide. For rayon processing, NaOH is also used.
- In the production of bleaching powder, Ca(OH)2, also referred to as slaked lime or calcium hydroxide, are used.
- Calcium hydroxide is used to produce dry mixes in painting or decoration.
- Magnesium hydroxide is widely used as a laxative, also known as magnesium milk. This, therefore, reduces residual acidity in the human intestine and is known as antacid thus.
- Ammonium hydroxide is a highly effective laboratory reagent.
- The residual soil acidity can be neutralized with slacked lime.

